Understanding the 2024-25 Flu Season in the United States
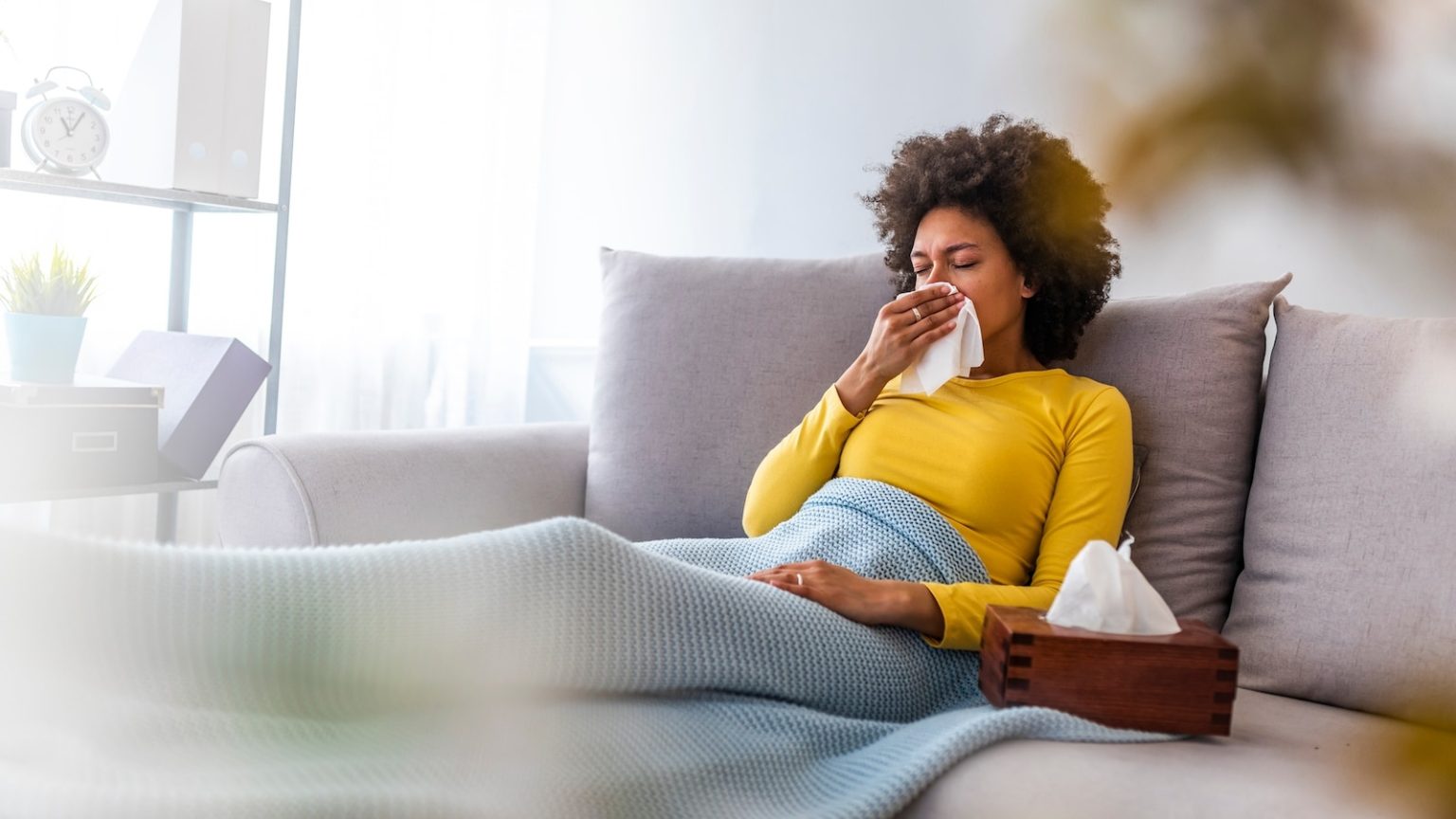
The 2024-25 flu season has been marked by significant activity across the United States, presenting a high severity classification from the CDC—the first since 2017-18. While flu activity remains elevated, recent data shows a promising decline, signaling a potential turning point in the season’s progression. This season’s impact has been profound, affecting millions and highlighting the importance of vigilance and preventive measures.
High Severity Season: A First Since 2017-18
This flu season’s classification as high severity underscores its significant impact on public health. The CDC’s designation applies to all age groups, indicating widespread and severe effects. In comparison to previous seasons, this year’s flu has been particularly challenging, with elevated activity persisting across the nation. The classification serves as a reminder of the virus’s unpredictable nature and the need for continued caution.
Declining Flu Activity: A Glimmer of Hope
Recent weeks have shown a decrease in flu-related visits to healthcare providers, with a drop from 7.7% to 6.8% in doctor visits and from over 8% to 6.4% in emergency department visits. While flu tests remain positive at 26.9%, this marks a decrease from the previous weeks’ 31.4%, suggesting a gradual easing of the flu’s grip. These trends, while cautiously optimistic, emphasize the ongoing need for public health strategies to manage the virus’s spread.
Impact on Public Health: The Numbers Behind the Season
The flu’s impact this season has been substantial, with over 33 million illnesses, 430,000 hospitalizations, and 19,000 deaths estimated by the CDC. Sadly, 86 pediatric deaths have been reported, including 18 in the week ending February 15. These statistics highlight the flu’s severity and the importance of understanding its effects on vulnerable populations, particularly children and the elderly.
Concurrent Respiratory Viruses: COVID-19 and RSV
Amidst the flu’s prevalence, other respiratory viruses such as COVID-19 and RSV have also been active. While COVID-19 activity is elevated, it remains stable with low emergency department visits. RSV, though declining, continues to affect populations, particularly the young and elderly. This convergence of viruses underscores the complexity of managing respiratory illnesses and the importance of comprehensive preventive measures.
Vaccination Rates: A Call to Action
Despite the severity of the season, vaccination rates remain concerning. Only 45.3% of adults have received the flu vaccine, and just 23.1% have been vaccinated against COVID-19. For RSV, 46.7% of seniors have been vaccinated, while a mere 12.1% of children have received the updated COVID-19 vaccine. Public health experts emphasize the importance of increasing these rates to mitigate future outbreaks and protect vulnerable populations.
Conclusion: Moving Forward with Prevention
As the flu season shows signs of decline but remains a significant concern, the focus must shift to prevention and preparedness. Vaccination is a critical tool in reducing the impact of respiratory viruses, and improving rates is essential. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can contribute to a healthier community, underscoring the importance of collective action against infectious diseases.