Breaking Discovery: Europe’s Euclid Space Telescope Uncovers Rare Einstein Ring Around Nearby Galaxy
A Rare Celestial Phenomenon Revealed
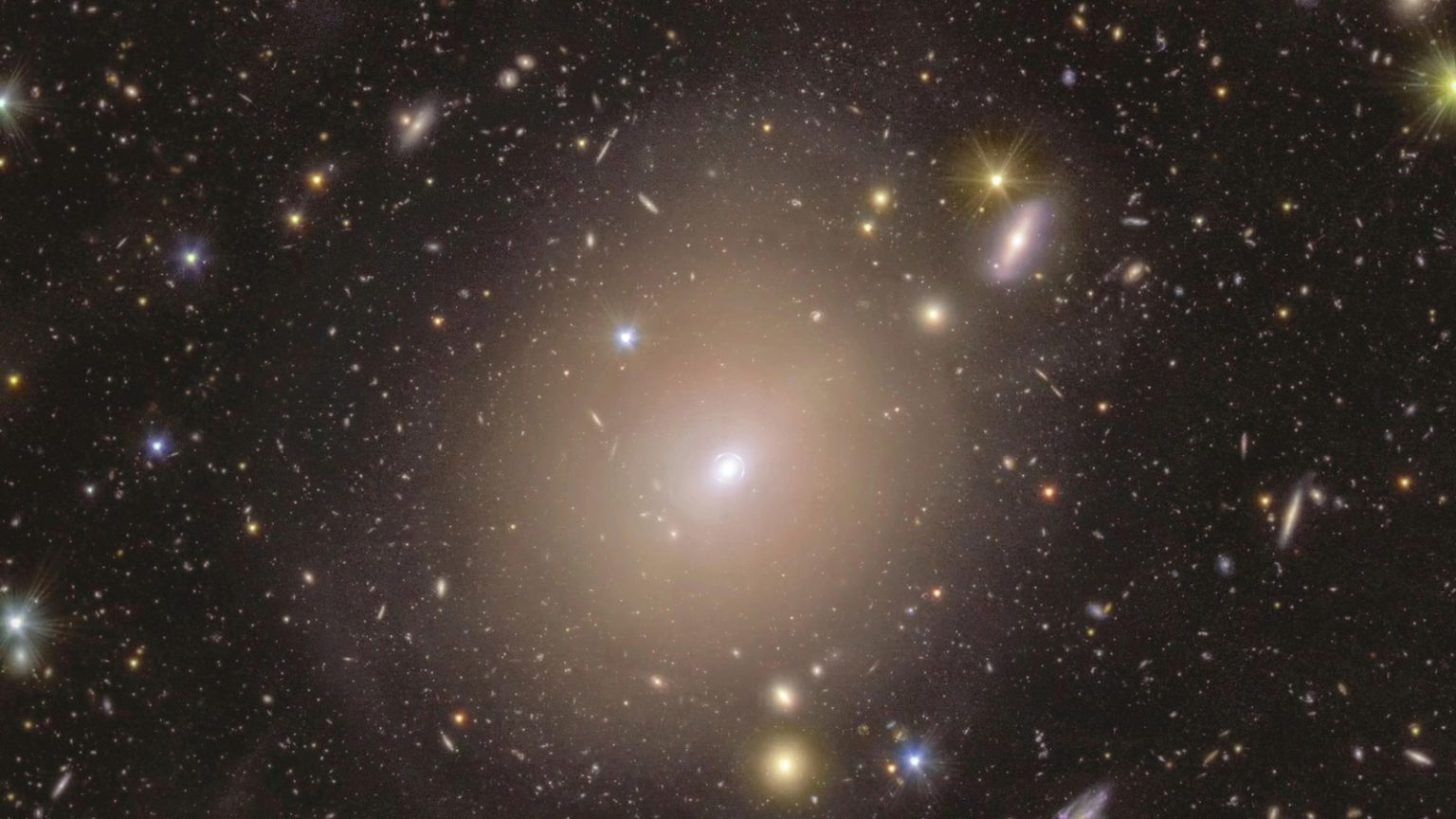
In an extraordinary breakthrough, Europe’s Euclid space telescope has made a remarkable discovery that is sending shockwaves through the astronomical community. Astronomers announced on Monday that the telescope has detected a rare and dazzling halo of light, known as an Einstein ring, surrounding a galaxy relatively close to Earth. This phenomenon, observed around a galaxy located 590 million light-years away in the constellation Draco, has left scientists both surprised and thrilled. The discovery was published in the prestigious journal Astronomy and Astrophysics, marking a significant milestone in our understanding of the universe.
The Einstein Ring: A Celestial Masterpiece
The Einstein ring is a breathtaking sight, a perfect circle of bright light encircling the galaxy. This phenomenon is not a simple trick of the light but rather the result of a complex interplay of gravity and light. The ring is formed when the light from a much more distant galaxy, located over 4 billion light-years away, bends around the closer galaxy due to the warping of spacetime caused by the galaxy’s massive gravitational field. This process, known as gravitational lensing, is a direct prediction of Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity, hence the name "Einstein ring."
Gravitational Lensing: The Science Behind the Magic
Gravitational lensing occurs when a massive object, such as a galaxy, bends the light from a more distant object behind it. This bending happens because the mass of the foreground object warps the fabric of spacetime, causing the light to follow a curved path. In the case of an Einstein ring, the alignment between the observer, the foreground galaxy, and the background galaxy is nearly perfect, resulting in a striking ring of light. This phenomenon is not only a visual marvel but also a powerful tool for scientists to study the distribution of mass in the universe, including the elusive dark matter.
A Surprising Discovery with Far-Reaching Implications
The galaxy at the center of the Einstein ring has been known to astronomers for over a century, yet the discovery of the ring around it has come as a surprise. This highlights how much still remains to be discovered in our universe, even in regions that have been studied extensively. The proximity of the galaxy to Earth, by cosmic standards, makes this discovery particularly valuable. "All strong lenses are special because they’re so rare, and they’re incredibly useful scientifically," said Dr. Conor O’Riordan, the lead author of the study and a researcher at Germany’s Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics. "This one is particularly special because it’s so close to Earth and the alignment makes it very beautiful."
The Euclid Mission: Unveiling the Universe’s Secrets
The discovery was made possible by the Euclid space telescope, a state-of-the-art observatory launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida, in 2023. Euclid is a collaboration between the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA, with a primary mission to study the universe’s dark energy and dark matter. Dark energy is the mysterious force driving the accelerating expansion of the universe, while dark matter is the invisible substance that makes up most of the universe’s mass. By studying phenomena like gravitational lensing, Euclid aims to shed light on these enigmatic entities and their role in shaping the cosmos.
Conclusion: A New Window to the Universe
The discovery of the Einstein ring is not just a stunning visual achievement but also a reminder of the awe-inspiring complexity and beauty of the universe. It underscores the importance of continued exploration and the role of advanced instruments like the Euclid telescope in unraveling the universe’s mysteries. As scientists continue to study this phenomenon, they may uncover new insights into the nature of dark matter and dark energy, ultimately deepening our understanding of the cosmos and our place within it. This discovery is a testament to human curiosity and the boundless wonders waiting to be discovered in the vast expanse of space.