How Modern Technology is Revolutionizing March Madness Bracket Predictions
The Rise of Robot Bracketologists
March Madness has long been one of the most unpredictable and exciting sporting events in America, with millions of fans filling out brackets each year in hopes of predicting the perfect tournament outcome. Traditionally, these predictions have been based on gut feelings, team loyalty, statistical analysis by human experts, or simply picking based on mascot preferences. However, a new player has entered the bracket-prediction game: artificial intelligence and robotics. An innovative office has decided to embrace the future by utilizing robots and AI technology to make their March Madness picks, representing a fascinating intersection of sports, technology, and workplace culture that demonstrates how automation and machine learning are penetrating even our leisure activities.
This groundbreaking approach to bracket selection reflects a broader trend of AI integration into everyday life. The office in question has programmed sophisticated algorithms and robotic systems to analyze vast amounts of basketball data, from player statistics and team performance metrics to historical tournament outcomes and even coaching tendencies. By removing human bias and emotion from the equation, these technological tools promise to deliver predictions based purely on data-driven insights. The experiment raises intriguing questions about the role of technology in sports prediction and whether cold, calculated machine logic can truly outperform human intuition when it comes to the beautiful chaos that defines March Madness.
How the AI and Robotic Systems Work
The technology deployed for this unique bracket challenge involves multiple layers of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms working in concert. The AI systems begin by ingesting enormous datasets that include decades of college basketball statistics, tournament results, individual player performance metrics, team rankings throughout the season, strength of schedule analysis, and countless other variables that might influence game outcomes. Machine learning models then identify patterns and correlations within this data that might be invisible or too complex for human analysts to detect. These patterns help the AI understand which factors most reliably predict tournament success.
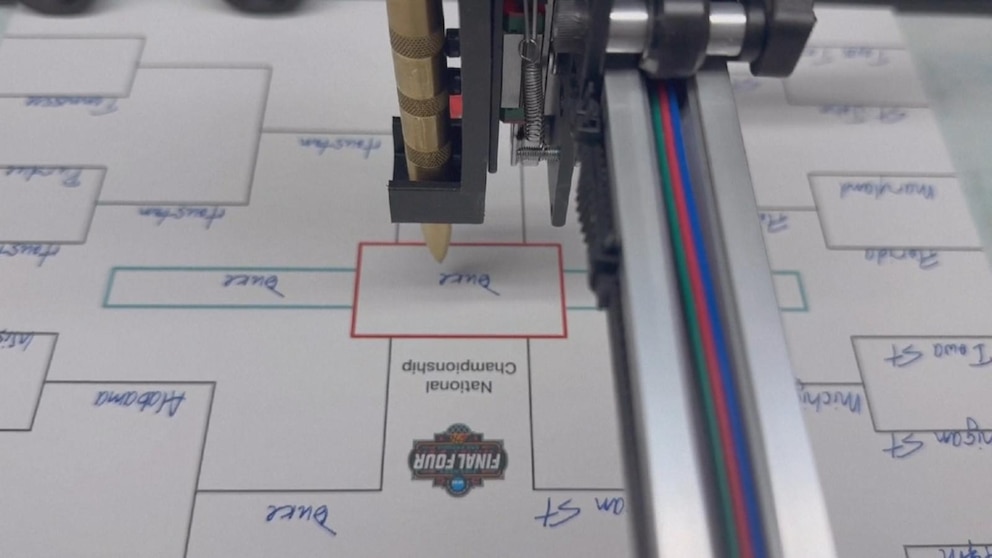
The robotic component adds another dimension to the selection process. While the AI handles the computational heavy lifting, the robots provide a physical interface and decision-making mechanism that brings the predictions to life. Some offices have programmed robots to physically fill out bracket sheets based on the AI’s recommendations, while others have created more interactive systems where robots can “discuss” their picks or even compete against each other using different algorithmic approaches. The robots might use computer vision to read bracket formats, mechanical systems to mark selections, and speech synthesis to explain their reasoning—creating an entertaining and educational experience for the humans watching the process unfold.
What makes this approach particularly sophisticated is the use of ensemble methods, where multiple AI models work simultaneously using different analytical frameworks. One algorithm might focus heavily on recent team performance and momentum, while another emphasizes historical tournament success of similar teams. A third might specialize in identifying upset potential by analyzing matchup-specific advantages. The system then aggregates these various perspectives, weighing each according to its historical accuracy, to produce final predictions that theoretically benefit from diverse analytical viewpoints. This mirrors how human bracket pools often benefit from diverse opinions and approaches.
The Human Element: Why People Are Embracing Robot Predictions
You might wonder why an office would turn to robots and AI for something as enjoyable and personal as filling out a March Madness bracket. The answer reveals interesting insights about modern workplace culture and our relationship with technology. For many participants, the robot bracket represents a fun experiment that brings a fresh twist to an annual tradition. Rather than replacing human participation, the technological approach adds a new competitor to the office pool—one that can be cheered for, rooted against, or simply observed with curiosity to see whether data truly triumphs over intuition.
There’s also an educational component that appeals to many workplaces, especially those in tech industries or data-driven fields. Watching AI and robots make March Madness predictions provides an accessible, low-stakes way to understand how these technologies work and what they can (and cannot) do well. Unlike deploying AI in critical business operations where mistakes have serious consequences, bracket predictions offer a perfect sandbox environment for exploring artificial intelligence capabilities. Employees can observe firsthand how algorithms process information, make decisions under uncertainty, and adapt when unexpected results occur—all within the familiar, entertaining context of college basketball.
Additionally, having a robot participant levels the playing field in office pools where some employees might know little about college basketball. Rather than feeling pressured to research teams or embarrassed by their lack of sports knowledge, these employees can align themselves with the robot’s picks or use them as a starting point for their own brackets. This inclusive aspect helps ensure that March Madness office pools remain fun social events rather than competitions that only engage the serious sports fans in the workplace.
Performance Results: Can Machines Really Beat Human Intuition?
The million-dollar question, of course, is whether these high-tech approaches actually work better than traditional bracket-filling methods. The results have been decidedly mixed, which actually tells us something important about both the nature of March Madness and the current limitations of AI. In some office competitions, robot brackets have performed impressively, especially in the early rounds where favored teams typically advance according to statistical expectations. AI systems excel at identifying which lower seeds have genuine upset potential based on metrics like efficiency ratings, player experience, and stylistic matchups—often outperforming casual fans who might pick upsets randomly or based on superficial factors.
However, March Madness earns its name for good reason. The tournament is famous for Cinderella stories, improbable runs, and upsets that defy all conventional wisdom and statistical modeling. These are precisely the moments where AI struggles, because truly unprecedented events by definition lack the historical data patterns that machine learning relies upon. A robot might correctly calculate that a 15-seed has a 5% chance of beating a 2-seed, but it cannot account for a star player having the game of their life, a crucial last-second shot, or the intangible momentum that builds when an underdog starts believing in themselves. These human elements—emotion, clutch performance under pressure, inspiration—remain difficult for algorithms to quantify and predict.
Interestingly, some of the most successful approaches combine human and artificial intelligence, creating hybrid brackets that leverage the strengths of both. In these systems, AI handles the statistical analysis and identifies key factors, but humans make final decisions about upsets and championship picks based on intangibles like coaching, team chemistry, or tournament experience. This collaboration between human intuition and machine calculation often outperforms either approach alone, suggesting that the future of sports prediction—and perhaps decision-making in many fields—lies not in choosing between human and artificial intelligence, but in finding effective ways to combine them.
Broader Implications: What This Tells Us About AI in Society
While using robots to fill out March Madness brackets might seem like a novelty or publicity stunt, it actually serves as a microcosm for larger conversations about artificial intelligence in society. The bracket challenge highlights both the impressive capabilities of modern AI and its current limitations in a context where the stakes are low and the outcomes are quickly evident. This makes it an ideal test case for understanding where AI excels and where human judgment remains superior.
The experiment demonstrates that AI performs best in domains with clear rules, abundant historical data, and quantifiable variables—all characteristics that describe much of March Madness basketball. Yet it also shows that AI still struggles with rare events, rapidly changing contexts, and scenarios where intangible human factors prove decisive. These insights translate directly to real-world AI applications in business, healthcare, finance, and other fields where organizations must decide which tasks to automate and which require human oversight.
Furthermore, the generally positive reception of robot bracketologists in office settings suggests that people are becoming more comfortable with AI as a presence in daily life, provided it’s introduced in friendly, non-threatening ways. By framing AI as a colleague or competitor rather than a replacement, these March Madness experiments help demystify the technology and build familiarity. The key seems to be positioning AI as a tool that augments rather than eliminates human participation—a lesson that organizations would do well to remember as they implement automation across various functions.
The Future of Sports Prediction and AI Integration
Looking ahead, the integration of AI and robotics into March Madness bracket selection is likely just the beginning of a broader transformation in how we engage with sports and predictions. As these technologies become more sophisticated and accessible, we can expect to see increasingly advanced prediction systems that incorporate real-time data from games in progress, social media sentiment analysis, biometric data about player fatigue and stress levels, and even weather conditions that might affect team travel. The AI systems of tomorrow might watch games as they unfold, updating probability models moment by moment and offering live insights that enhance rather than replace the human viewing experience.
Beyond bracket predictions, these technologies are already reshaping sports in other ways. Professional teams use AI to evaluate talent, plan strategies, prevent injuries, and optimize training regimens. Broadcasting companies employ machine learning to create personalized viewing experiences and generate automated highlights. Fantasy sports platforms leverage algorithms to provide player recommendations and matchup analysis. The office using robots for March Madness picks is participating in this larger revolution, using a beloved annual tradition as an opportunity to explore what technology can bring to sports fandom.
Ultimately, the story of robot bracketologists is not about replacing human participation in March Madness or proving that machines are superior to people at prediction. Instead, it’s about exploration, education, and entertainment—using new tools to add fresh dimensions to familiar experiences. Whether the robots win the office pool or finish in last place, they’ve already succeeded in their most important function: sparking conversations about technology, engaging colleagues in playful competition, and reminding us that innovation works best when it enhances rather than eliminates the human elements that make activities like March Madness meaningful. As we continue integrating AI into more aspects of life, maintaining this balanced perspective—embracing technological capabilities while preserving human connection, judgment, and joy—will be essential to creating a future where humans and machines each contribute what they do best.